

The Role of Variable Rate Application in Sustainable Farming
Variable rate application (VRA) technology uses precision agriculture to apply fertilizers and pesticides based on specific field needs. Dividing land into management zones, VRA optimizes resource use and crop productivity. Doktar’s Orbit app creates prescription maps, enhancing resource efficiency and reducing environmental impact, despite challenges in initial investment and data accuracy.
Published on 14 June 2023
Understanding Variable Rate Application: What Is Variable Rate Application?
Variable rate application technology, or VRA, is a precision agriculture technique that involves applying different quantities of inputs, such as fertilizers or pesticides, at specific locations within a field based on site-specific needs. Unlike conventional farming practices that apply a uniform rate across the entire field, VRA utilizes advanced technology and data analysis to determine the optimal amount of inputs required for each specific area. This tailored approach ensures that crops receive the necessary resources while minimizing waste.
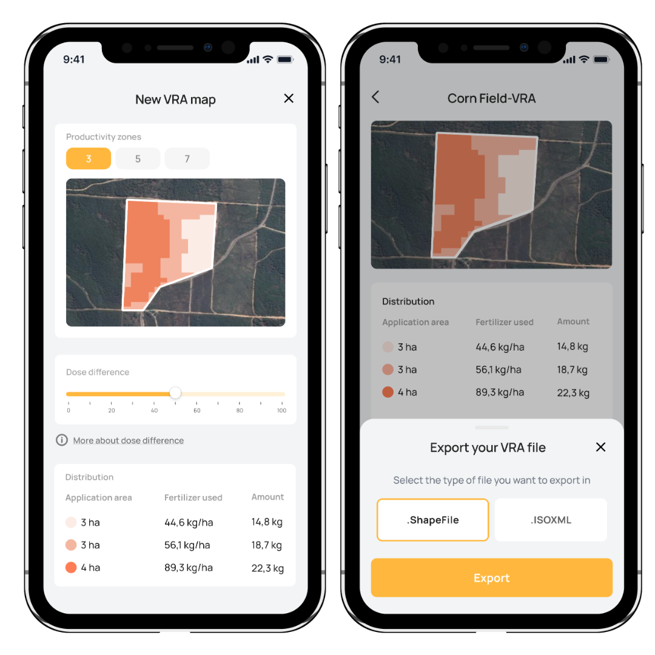
To carry out VRA, the land is divided into different managment zones refering to the varying level of input application to be carried out. Doktar’s field scouting app Orbit leverages satellite imagery to divide fields into three, five or seven distinct zones. These zones are created by analyzing crucial factors like vegetation indices, soil moisture, and crop health. Tailoring your approach to each zone enables you to address specific needs and challenges, maximizing your crop's potential. Orbit then creates prescription maps that specify the recommended variable rate fertilizer application rates for each zone. The application rates are tailored to address the specific needs and requirements of each zone, optimizing resource utilization and maximizing crop productivity.

VRA and Resource Efficiency
One of the key benefits of VRA is its ability to enhance resource efficiency on farms. By utilizing precise data on soil conditions, crop requirements, and historical yield maps, farmers can make informed decisions regarding the application of fertilizers and other inputs. VRA technology enables them to create variable rate application maps, which guide equipment to apply the appropriate amounts at the right locations. This targeted approach prevents over-application and under-application, optimizing resource usage and reducing costs for farmers.
Reducing Environmental Impact with VRA
Sustainable farming practices aim to minimize the negative impact of agriculture on the environment. VRA plays a crucial role in achieving this goal by reducing the environmental footprint of farming operations. By applying fertilizers and pesticides precisely where they are needed, VRA minimizes the potential for runoff and leaching, preventing water pollution and protecting ecosystems. Furthermore, by minimizing excess application, VRA helps to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions associated with the production and use of agricultural inputs.
Challenges and Opportunities in Sustainable Farming with VRA
While VRA offers numerous benefits, its adoption in sustainable farming does come with challenges. The initial investment required for VRA technology and equipment can be a barrier for some farmers. Additionally, the collection and analysis of accurate data on soil properties, nutrient levels, and crop requirements can be complex. The Orbit app however, helps with these challanges by asking farmers the previous fertilizer application dates, and creates a prescription map based on the NDVI data from those dates.
One of the key benefits of VRA through Orbit is its ability to provide accurate recommendations for fertilizer application. By precisely understanding the nutrient requirements of each zone, Orbit suggests optimized fertilizer rates for different areas of your field. Implementing these recommendations can lead to impressive results, with farmers experiencing up to 5% savings on their fertilizer usage.
Real-World Examples of VRA in Sustainable Farming
Numerous real-world examples highlight the success of VRA in sustainable farming. For instance, farmers have achieved substantial reductions in fertilizer use. By implementing VRA, they have been able to identify nutrient deficiencies, optimize application rates, and enhance overall nutrient management practices. Similarly, VRA has proven effective in managing pests and diseases, reducing the need for broad-spectrum pesticides and minimizing the impact on beneficial organisms.
When it comes to Orbit, the app goes beyond just providing recommendations; it ensures their practical real-life implementation as well. The fertilization recommendation maps generated by VRA can be seamlessly integrated into tractors and other agricultural equipment. This integration allows for precise and automated application, saving time and effort. Alternatively, if a semi-manual approach ‘s followed, Orbit also supports the use of the maps as a guide during application, allowing for flexibility and control.
With Orbit, every decision made is also captured for future reference. All VRA maps, including zoning, recommendations, and application records, are meticulously recorded. This retrospective feature enables farmers to track and analyze the effectiveness of strategies over time. By learning from past experiences, farmers can continually optimize agricultural practices, achieving greater efficiencies and higher yields with each season.
Conclusion
As sustainable farming practices continue to evolve, Variable Rate Application in precision agriculture emerges as a powerful tool in the industry. By fine-tuning the application of inputs through VRA technology, farmers can optimize resource efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and improve overall farm productivity. Although challenges exist, the potential for VRA in sustainable farming is undeniable. With further advancements in technology, increased accessibility, and knowledge sharing, VRA has the ability to revolutionize the way we cultivate our land, ensuring a more sustainable and productive future for agriculture.
For those interested in exploring how Doktar's innovative solutions can transform your agricultural practices, visit our website for detailed information on all our products. Stay updated with the latest developments by following us on Instagram and LinkedIn, where we share insights, tips, and updates about our technologies and their impact on modern farming.

Agriculture Technology and Data-Driven Harvests
The convergence of agriculture technology and data-driven solutions represents the next frontier of innovation in farming. With companies like Doktar leading the way, farmers can leverage these advancements to improve productivity, reduce environmental impact, and secure a more sustainable future for agriculture. Whether through precision agriculture, sustainable agriculture, or cutting-edge smart agriculture technology, the future of farming is bright, and data is at the heart of this transformation. Technology's positive impact on this future should inspire and motivate us all.

Integrating Crop Health Monitoring Systems for Better Farm Management
Crop health monitoring systems revolutionize modern agriculture by enabling real-time insights into plant health, reducing losses, and promoting sustainability. Tools like Doktar’s CropMap and Orbit integrate advanced technologies, empowering farmers with data-driven decisions. By enhancing efficiency and sustainability, these systems are essential for future-proofing agricultural operations.

Modern Agriculture: Innovative Solutions to Combat Global Food Insecurity
Modern agriculture combats global food insecurity with precision agriculture, sustainable practices, and biotechnology. Tools like IoT, automation, and crop innovations optimize resource use, enhance resilience, and ensure stable food supplies. By integrating smart technologies, agribusinesses address challenges like climate change and resource scarcity, paving the way for a sustainable food future.
