
Insider's Guide to CropMap Tech
CropMap is a groundbreaking invention that leverages satellite imagery, machine learning, and high-quality ground-truth data to revolutionize crop classification. This advanced technology addresses and conquers existing solutions' limitations in the field.
Published on 20 December 2023
In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, precision is key. The ability to accurately classify and monitor crops not only helps maximize yield. It also contributes significantly to efficient resource allocation and decision-making for businesses such as agricultural input providers and food processors. Traditional crop classification methods have often fallen short of the mark, struggling with accuracy and efficiency, especially in large-scale and commercial applications. However, CropMap is changing the game.
CropMap: A Crop Classification Innovation
CropMap is a groundbreaking invention that leverages satellite imagery, machine learning, and high-quality ground-truth data to revolutionize crop classification. This advanced technology addresses and conquers existing solutions' limitations in the field.
(CropMap 2022 Spain, Corn)
The Challenges in Crop Classification
The primary challenge in current crop classification pipelines is accuracy. When applied to large regions, existing algorithms often lack the precision required for industrial or commercial applications, leading to significant deviations in total area. Even high-value crops like tomatoes face accuracy issues, impacting economic assessments. The technical challenges contributing to these problems include:
-
Temporal Resolution & Cloud Cover: The frequency of satellite imagery capture must be high enough to track changes in crop development, but cloud cover can hinder image quality, resulting in a lower effective temporal resolution with irregular imagery frequency.
-
Ground Truth Data: The accuracy of crop identification depends on the availability and quality of ground-truth data, particularly for high-value crops such as tomatoes.
-
Data Processing: Current technology often employs little pre-processing and uses complex algorithms to handle raw data, which can be suboptimal for machine learning.
-
Spectral Resolution: High spectral resolution is necessary for accurately distinguishing different crop types based on their unique spectral signatures.
-
Clarity & Usability of Images: Atmospheric interference and noise can impede the ability to obtain clear and detailed information from satellite data, hindering accurately delineating field boundaries and crop classifications.

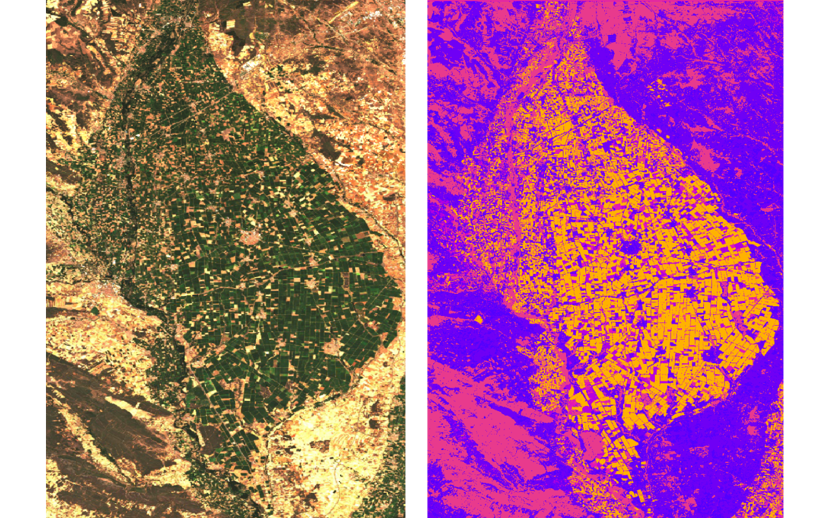
(CropMap, 2023 Orange: Wheat, Yellow: Sunflower, Blue: Sugarbeet)
Innovations Brought by CropMap
This year, the CropMap team has processed over 50 billion lines of code, introducing innovative approaches to overcome these challenges:
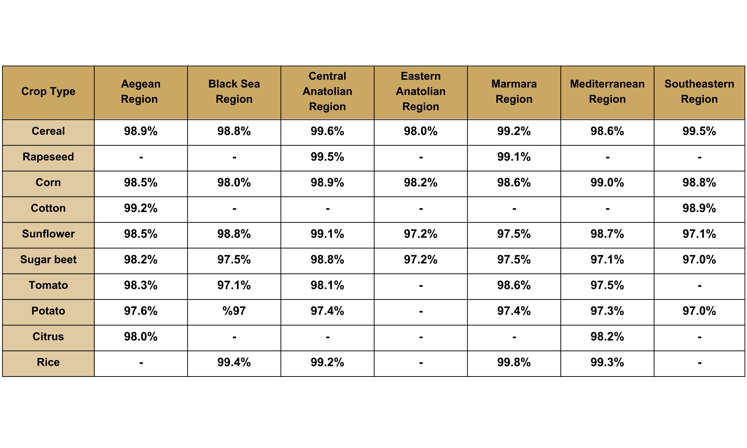
Below is a detailed accuracy showcasing CropMap's exceptional precision in crop classification across various regions and crop types. Near 99% accuracy is important for:
-
Market Analysis: Knowing the types and quantities of crops in a particular region allows for a more accurate analysis of supply and demand dynamics. This information is vital for predicting market trends and deciding when and where to sell or buy crops.
-
Risk Management: Stakeholders can use accurate information about crop types and plantation areas to assess and manage risks associated with price fluctuations. This enables them to make more informed decisions about when to sell their produce or when to invest in certain crops.
-
Policy Planning: Governments and policymakers can use accurate crop classification data to formulate effective agricultural policies. This includes planning for subsidies, trade regulations, and other measures influencing crop prices and market stability.
Empowering Agriculture with CropMap
CropMap is not just a technological leap; it's a transformative force in agriculture. Overcoming the challenges in crop classification empowers the industry with the precision and data needed to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and drive agricultural innovation forward. With CropMap, the future of agriculture is brighter than ever.
For those interested in exploring how Doktar's innovative solutions can transform your agricultural practices, visit our website for detailed information on all our products. Stay updated with the latest developments by following us on Instagram and LinkedIn, where we share insights, tips, and updates about our technologies and their impact on modern farming.

Agriculture Technology and Data-Driven Harvests
The convergence of agriculture technology and data-driven solutions represents the next frontier of innovation in farming. With companies like Doktar leading the way, farmers can leverage these advancements to improve productivity, reduce environmental impact, and secure a more sustainable future for agriculture. Whether through precision agriculture, sustainable agriculture, or cutting-edge smart agriculture technology, the future of farming is bright, and data is at the heart of this transformation. Technology's positive impact on this future should inspire and motivate us all.

Integrating Crop Health Monitoring Systems for Better Farm Management
Crop health monitoring systems revolutionize modern agriculture by enabling real-time insights into plant health, reducing losses, and promoting sustainability. Tools like Doktar’s CropMap and Orbit integrate advanced technologies, empowering farmers with data-driven decisions. By enhancing efficiency and sustainability, these systems are essential for future-proofing agricultural operations.

Modern Agriculture: Innovative Solutions to Combat Global Food Insecurity
Modern agriculture combats global food insecurity with precision agriculture, sustainable practices, and biotechnology. Tools like IoT, automation, and crop innovations optimize resource use, enhance resilience, and ensure stable food supplies. By integrating smart technologies, agribusinesses address challenges like climate change and resource scarcity, paving the way for a sustainable food future.
