

From Fields to Satellites: Remote Sensing in Agriculture
Remote sensing gathers data about objects or phenomena from a distance using sensors, typically on satellites or drones. It enables real-time monitoring of environmental conditions, crop health, and climate change. In agriculture, it helps in detecting issues like disease outbreaks and water stress, aiding timely interventions and optimizing crop management.
Published on 14 June 2023
What is remote sensing? What is the best definition of remote sensing?
Remote sensing refers to the process of gathering information about an object or phenomenon from a distance, without physical contact. It involves measuring or collecting data using sensors that are not in direct proximity to the subject being studied.
How is Remote Sensing Used?
In modern times, when we mention remote sensing, satellites often come to mind. However, remote sensing examples include various technologies such as medical imaging tools like sonographs and x-rays, which gather data without physical contact too. The application of remote sensing is endless and typically, remote sensing involves the use of satellites, aircrafts, drones, or ground-based sensors to capture environmental data for a range of applications, such as climate change monitoring and agricultural modeling.
How does remote sensing work? What is a Remote Sensing Satellite? Is satellite imagery remote sensing?
The functioning of remote sensing relies on capturing electromagnetic radiation emitted or reflected from the Earth's surface or atmosphere. Sensors on remote sensing satellites detect this radiation and convert it into digital data, which can then be analyzed and interpreted to extract valuable information about the environment. This data can be utilized to create maps, analyze trends, and detect changes over time.

What is Remote Sensing Used For?
In the realm of agriculture, remote sensing imaging has revolutionized the field by enabling the measurement of crop productivity and health. It has diverse applications, such as aiding in the development of insurance products for small farmers and serving as a market insight tool through platforms like CropMap.
Additionally, remote sensing data obtained from satellites is utilized in field health monitoring apps like Orbit, which provides real-time monitoring of crop growth and weather patterns. Remote sensing data acts as an accurate early warning system, facilitating timely updates to farming practices, evaluation of irrigation system efficiency, assessment of pesticide effectiveness, monitoring of physical farming techniques, identification of pest infestations, and assessing the risk of droughts or floods.
High-frequency multispectral remote sensing contributes to monitoring forest and agriculture projects, predicting agricultural emergencies, and detecting changes in food supply and rural growth. These applications help promote sustainable agricultural practices and environmental conservation.
What are the advantages of Remote Sensing?
Remote sensing technology offers several advantages for agriculture, including the ability to map soil properties and classify crop species. It allows farmers to remotely monitor their fields and identify issues such as disease outbreaks, water stress, or nutrient deficiencies before they become visible to the naked eye.
Timely detection of problems with satellite remote sensing enables farmers to take necessary action to prevent crop loss and improve yields. Utilizing remote sensing technology like the Orbit app, farmers can remotely scout their fields, detect issues, and make data-driven decisions about crop management. Remote sensing in agriculture allows farmers to monitor the health and growth of plants without frequent trips to their farms, optimizing field visits to locations where difficulties are noticed.
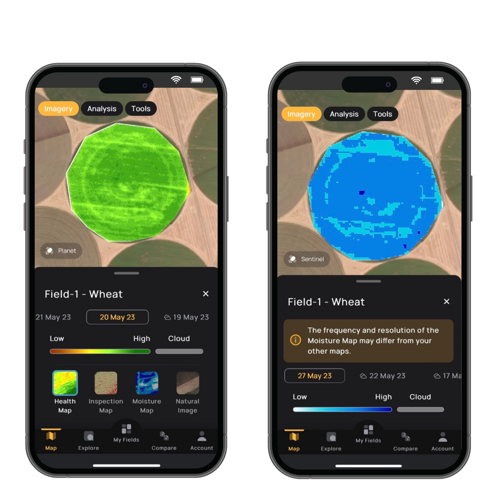
What is Remote Sensing Used For?
In the realm of agriculture, remote sensing imaging has revolutionized the field by enabling the measurement of crop productivity and health. It has diverse applications, such as aiding in the development of insurance products for small farmers and serving as a market insight tool through platforms like CropMap.
Additionally, remote sensing data obtained from satellites is utilized in field health monitoring apps like Orbit, which provides real-time monitoring of crop growth and weather patterns. Remote sensing data acts as an accurate early warning system, facilitating timely updates to farming practices, evaluation of irrigation system efficiency, assessment of pesticide effectiveness, monitoring of physical farming techniques, identification of pest infestations, and assessing the risk of droughts or floods.
High-frequency multispectral remote sensing contributes to monitoring forest and agriculture projects, predicting agricultural emergencies, and detecting changes in food supply and rural growth. These applications help promote sustainable agricultural practices and environmental conservation.
What are the advantages of Remote Sensing?
Remote sensing technology offers several advantages for agriculture, including the ability to map soil properties and classify crop species. It allows farmers to remotely monitor their fields and identify issues such as disease outbreaks, water stress, or nutrient deficiencies before they become visible to the naked eye.
Timely detection of problems with satellite remote sensing enables farmers to take necessary action to prevent crop loss and improve yields. Utilizing remote sensing technology like the Orbit app, farmers can remotely scout their fields, detect issues, and make data-driven decisions about crop management. Remote sensing in agriculture allows farmers to monitor the health and growth of plants without frequent trips to their farms, optimizing field visits to locations where difficulties are noticed.
For those interested in exploring how Doktar's innovative solutions can transform your agricultural practices, visit our website for detailed information on all our products. Stay updated with the latest developments by following us on Instagram and LinkedIn, where we share insights, tips, and updates about our technologies and their impact on modern farming.

Agriculture Technology and Data-Driven Harvests
The convergence of agriculture technology and data-driven solutions represents the next frontier of innovation in farming. With companies like Doktar leading the way, farmers can leverage these advancements to improve productivity, reduce environmental impact, and secure a more sustainable future for agriculture. Whether through precision agriculture, sustainable agriculture, or cutting-edge smart agriculture technology, the future of farming is bright, and data is at the heart of this transformation. Technology's positive impact on this future should inspire and motivate us all.

Integrating Crop Health Monitoring Systems for Better Farm Management
Crop health monitoring systems revolutionize modern agriculture by enabling real-time insights into plant health, reducing losses, and promoting sustainability. Tools like Doktar’s CropMap and Orbit integrate advanced technologies, empowering farmers with data-driven decisions. By enhancing efficiency and sustainability, these systems are essential for future-proofing agricultural operations.

Modern Agriculture: Innovative Solutions to Combat Global Food Insecurity
Modern agriculture combats global food insecurity with precision agriculture, sustainable practices, and biotechnology. Tools like IoT, automation, and crop innovations optimize resource use, enhance resilience, and ensure stable food supplies. By integrating smart technologies, agribusinesses address challenges like climate change and resource scarcity, paving the way for a sustainable food future.
